The Critical Importance of Repeatability
in SLAM Lidar Mapping Systems for Surveying
Reading time: 5 Minutes
24/06/24 Written By Tom Warner
This white paper examines the importance of repeatability in SLAM systems, with a focus on surveying applications. As SLAM technology leverages Lidar sensors to provide high-resolution spatial data, the necessity of repeatable results becomes paramount. This paper explores the role of Post-Processing Kinematic (PPK) GPS in ensuring high levels of repeatability and discusses how a robust SLAM engine maintains accuracy in GPS-denied environments.
The VellusX SLAM Lidar system
SLAM technology has revolutionised the field of surveying by enabling the creation of detailed and precise maps while simultaneously tracking the position of the sensor. LIDAR sensors are central to these systems, providing accurate relative spatial data. However, the metric of global repeatability is often overlooked. This white paper examines the critical need for global repeatability in SLAM systems and considers the contributions of PPK GPS to the overall robustness of the system.
Repeatability, in the context of SLAM Lidar systems, refers to the system’s ability to produce consistent maps when surveying the same environment even if the trajectory changes between sessions. Achieving high repeatability means that multiple surveys of the same area yield nearly identical results with minimal deviations. This in turn ensures the reliability and global accuracy of the data.
Repeatability serves as a benchmark for verifying and validating the performance of SLAM systems. Without repeatability, it is challenging to determine whether a system is functioning correctly. This is particularly important in regulatory environments where accuracy and reliability are critical for compliance and safety.
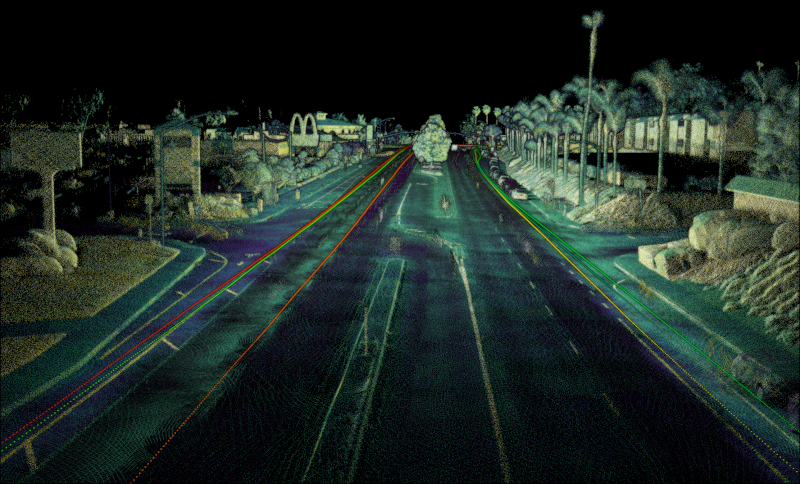
Three separate runs compared together
Cross-sections of three separate runs compared
Building Trust in Technology
For clients and stakeholders, repeatability is integral to building trust in SLAM technology. Whether it’s in geospatial surveying, construction planning, or infrastructure management, users need assurance that the technology will perform reliably under a wider array of scanning conditions. Repeatability provides the confidence that the system can be depended upon to deliver accurate and stable results, fostering greater adoption and investment in SLAM technologies.
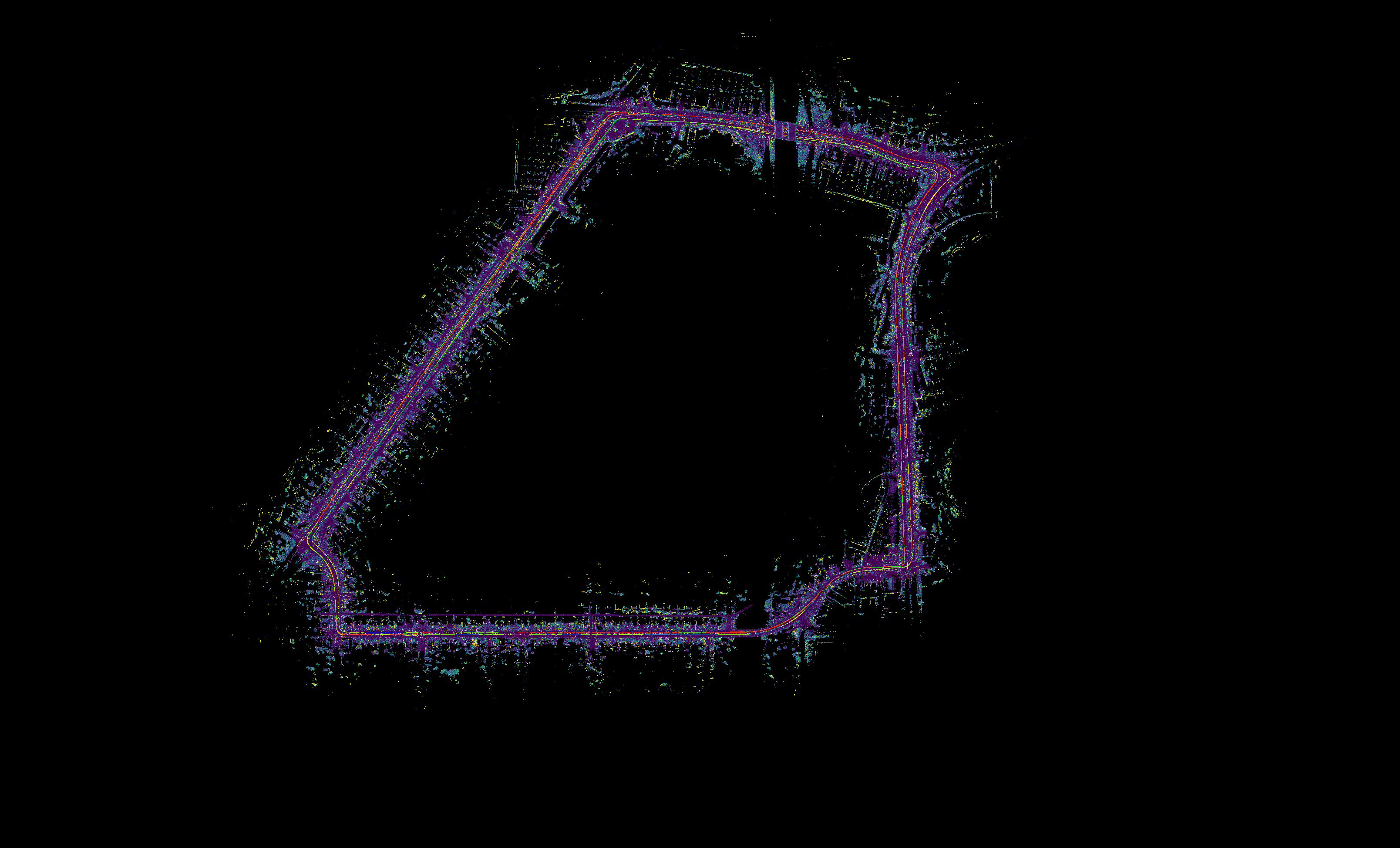
An overview of the three PPK-SLAM comparison runs
Role of PPK GPS
Post-Processing Kinematic (PPK) GPS is a technique used to enhance the accuracy of positioning data collected by GPS receivers. In surveying, PPK GPS is utilized to correct the raw positional data by comparing it with data from a reference station. This process significantly improves the accuracy and repeatability of the GPS data, which is critical for high-precision surveying tasks.
Integration with SLAM Systems
Integrating PPK GPS within the SLAM engine ensures that the positional data used for mapping is highly accurate. This integration helps to realign the sensor’s trajectory to compensate for drift. This ensures map accuracy with the actual geographic coordinates which in turn reduces discrepancies and enhances repeatability. PPK GPS provides a reliable positional reference that can correct any accumulated drift in the SLAM system, ensuring that repeated surveys of the same area yield consistent results.
Demonstration of repeatability from
three separate runs at a bridge
Precise PPK GPS enables the SLAM engine to realign the odometric trajectory to make it more accurate by redistributing any error that has been accumulating up until the PPK GPS observation. Since the PPK observation is a direct positional observation, it be used as a high-weighted constraint to ensure that the final SLAM solution is accurate in an absolute reference frame. By combining data from multiple sensors and employing sophisticated algorithms, robust SLAM engines can ensure high levels of accuracy and repeatability even in the absence of consistent GPS signals.
When constraints are transformed in to the SLAM reference frame, the observations are converted to local frame with a scale factor of 1. This enables the PPK GPS observations to also be used as a reference to reproject the map back into global reference frame for use by surveyors.
Repeatability is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental requirement for the success and reliability of SLAM Lidar mapping systems in surveying applications. The integration of PPK GPS enhances positional accuracy, while robust SLAM engines ensure reliability in GPS-denied environments. Neglecting repeatability can have far-reaching implications, potentially jeopardizing safety, efficiency, and stakeholder trust. As the technology continues to evolve and find new applications, prioritizing repeatability will be crucial in achieving the full potential of SLAM systems.